All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
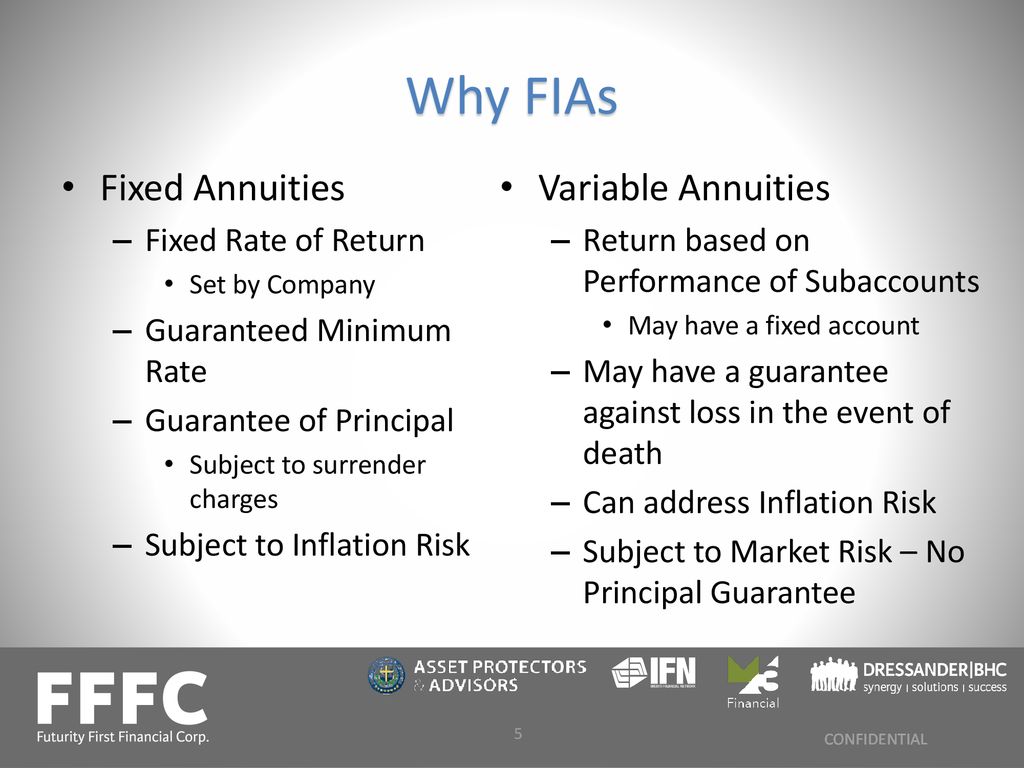
Equally as with a fixed annuity, the owner of a variable annuity pays an insurer a round figure or collection of repayments for the guarantee of a series of future settlements in return. As stated over, while a repaired annuity grows at an assured, continuous rate, a variable annuity grows at a variable price that depends upon the performance of the underlying investments, called sub-accounts.
During the buildup stage, possessions invested in variable annuity sub-accounts grow on a tax-deferred basis and are exhausted just when the agreement owner takes out those revenues from the account. After the build-up phase comes the income phase. With time, variable annuity assets need to theoretically increase in worth up until the agreement proprietor chooses she or he wish to start withdrawing money from the account.
The most significant concern that variable annuities usually existing is high cost. Variable annuities have a number of layers of fees and expenses that can, in aggregate, produce a drag of up to 3-4% of the contract's value each year.
Decoding Fixed Annuity Vs Equity-linked Variable Annuity Key Insights on Your Financial Future Defining the Right Financial Strategy Features of Smart Investment Choices Why Choosing the Right Financial Strategy Can Impact Your Future How to Compare Different Investment Plans: A Complete Overview Key Differences Between Different Financial Strategies Understanding the Key Features of Choosing Between Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity Who Should Consider Strategic Financial Planning? Tips for Choosing the Best Investment Strategy FAQs About Planning Your Financial Future Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Financial Strategy Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Growth Annuity A Beginner’s Guide to Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity A Closer Look at How to Build a Retirement Plan
M&E expenditure costs are calculated as a percentage of the agreement worth Annuity companies pass on recordkeeping and various other administrative expenses to the agreement proprietor. This can be in the type of a flat yearly charge or a percentage of the agreement worth. Management charges might be included as component of the M&E threat charge or may be evaluated separately.
These fees can range from 0.1% for easy funds to 1.5% or more for proactively handled funds. Annuity agreements can be personalized in a number of ways to serve the certain requirements of the agreement proprietor. Some common variable annuity bikers include ensured minimal buildup benefit (GMAB), assured minimum withdrawal benefit (GMWB), and ensured minimum income benefit (GMIB).
Variable annuity payments offer no such tax obligation reduction. Variable annuities have a tendency to be very ineffective cars for passing riches to the next generation because they do not appreciate a cost-basis modification when the original contract proprietor passes away. When the owner of a taxed investment account dies, the cost bases of the investments held in the account are gotten used to mirror the marketplace costs of those financial investments at the time of the owner's death.
Breaking Down Your Investment Choices A Comprehensive Guide to Variable Annuities Vs Fixed Annuities Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Retirement Plans Why Choosing the Right Financial Strategy Can Impact Your Future Annuities Fixed Vs Variable: How It Works Key Differences Between Different Financial Strategies Understanding the Rewards of Fixed Vs Variable Annuities Who Should Consider What Is Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity? Tips for Choosing the Best Investment Strategy FAQs About Planning Your Financial Future Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Indexed Annuity Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Your Options A Beginner’s Guide to Fixed Vs Variable Annuities A Closer Look at Fixed Vs Variable Annuities
For that reason, heirs can acquire a taxed investment portfolio with a "fresh start" from a tax perspective. Such is not the case with variable annuities. Investments held within a variable annuity do not obtain a cost-basis change when the initial owner of the annuity passes away. This suggests that any accumulated unrealized gains will be passed on to the annuity owner's heirs, in addition to the connected tax problem.
One considerable issue connected to variable annuities is the potential for disputes of rate of interest that may exist on the part of annuity salespeople. Unlike a financial consultant, that has a fiduciary obligation to make investment decisions that benefit the client, an insurance policy broker has no such fiduciary obligation. Annuity sales are extremely profitable for the insurance policy specialists who offer them since of high in advance sales compensations.
Many variable annuity agreements include language which positions a cap on the portion of gain that can be experienced by particular sub-accounts. These caps avoid the annuity owner from completely taking part in a portion of gains that might otherwise be enjoyed in years in which markets produce considerable returns. From an outsider's point of view, presumably that capitalists are trading a cap on investment returns for the previously mentioned assured flooring on financial investment returns.
As noted over, surrender fees can drastically restrict an annuity owner's capability to move possessions out of an annuity in the early years of the agreement. Even more, while a lot of variable annuities permit agreement proprietors to take out a specified quantity during the build-up stage, withdrawals past this amount usually cause a company-imposed charge.
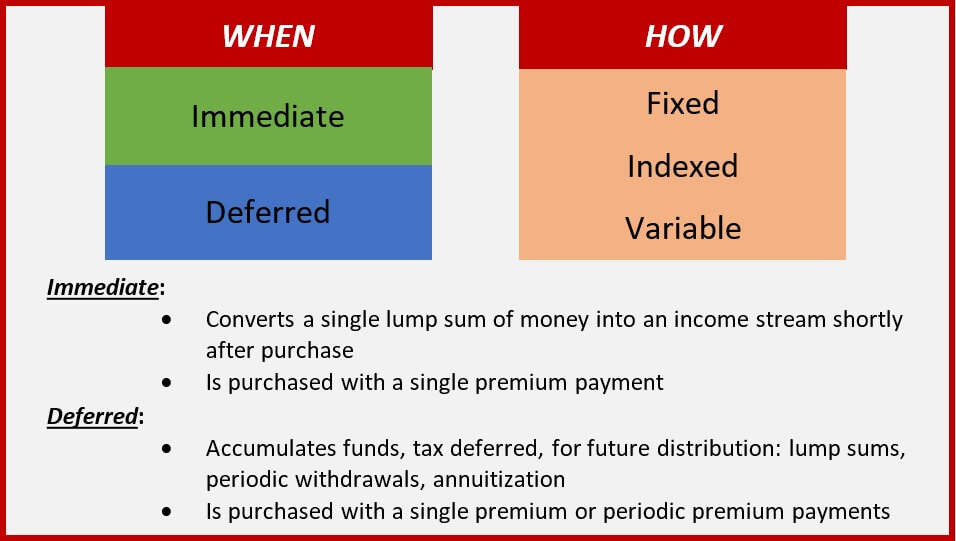
Withdrawals made from a set rate of interest investment option might also experience a "market worth change" or MVA. An MVA readjusts the worth of the withdrawal to show any kind of modifications in rates of interest from the moment that the money was purchased the fixed-rate option to the moment that it was withdrawn.

Frequently, even the salespeople that offer them do not totally comprehend just how they work, and so salespeople occasionally victimize a customer's feelings to sell variable annuities as opposed to the qualities and viability of the products themselves. We think that capitalists should totally comprehend what they possess and how much they are paying to possess it.
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices Defining What Is Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Retirement Plans Why Variable Vs Fixed Annuities Matters for Retirement Planning How to Compare Different Investment Plans: Simplified Key Differences Between Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Indexed Annuity Understanding the Key Features of Fixed Interest Annuity Vs Variable Investment Annuity Who Should Consider Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros And Cons? Tips for Choosing the Best Investment Strategy FAQs About Planning Your Financial Future Common Mistakes to Avoid When Planning Your Retirement Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros Cons A Beginner’s Guide to Fixed Vs Variable Annuity A Closer Look at Fixed Vs Variable Annuity
The same can not be claimed for variable annuity properties held in fixed-rate investments. These properties lawfully belong to the insurance business and would as a result be at risk if the business were to fail. Any kind of assurances that the insurance business has actually agreed to provide, such as an assured minimum income advantage, would certainly be in concern in the event of a company failing.
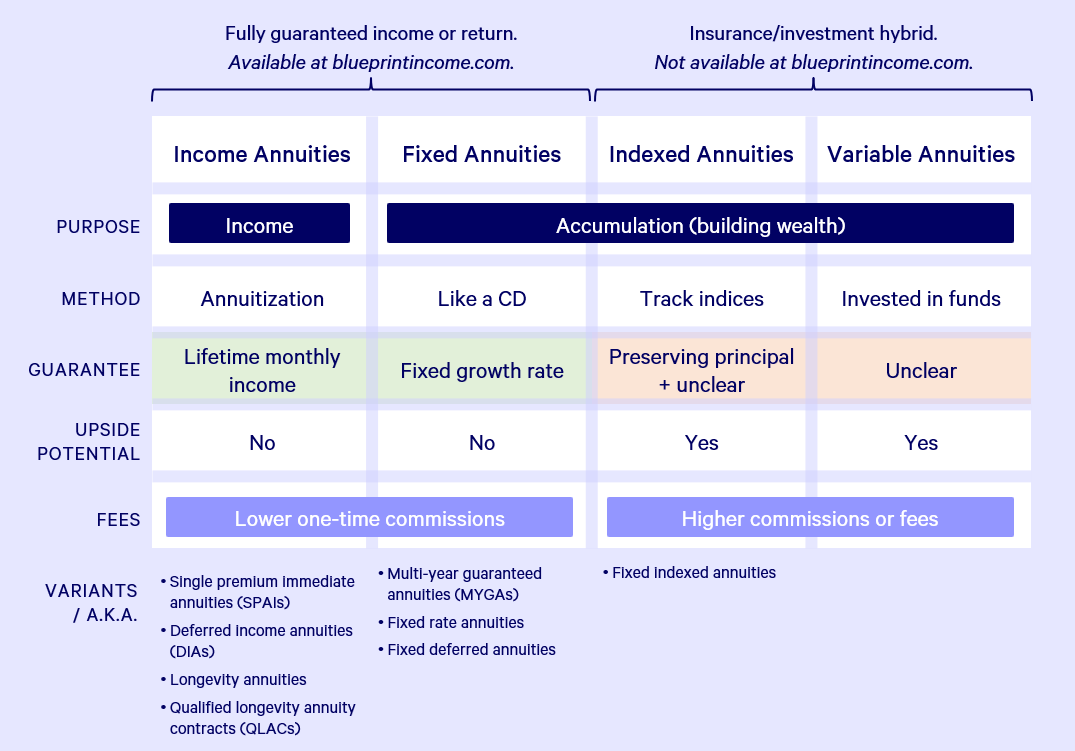
Potential purchasers of variable annuities ought to understand and think about the monetary problem of the providing insurance policy business before entering into an annuity contract. While the advantages and downsides of different types of annuities can be debated, the genuine issue bordering annuities is that of viability.
Besides, as the claiming goes: "Caveat emptor!" This post is prepared by Pekin Hardy Strauss, Inc. Tax-deferred annuity benefits. ("Pekin Hardy," dba Pekin Hardy Strauss Wide Range Monitoring) for informational functions only and is not meant as an offer or solicitation for business. The information and information in this article does not make up lawful, tax obligation, accounting, investment, or various other expert advice
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Breaking Down Your Investment Choices A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices Defining the Right Financial Strategy Pros and Cons of Various Financial Options Why Choosing the Right Financial Stra
Highlighting Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Everything You Need to Know About Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Defining the Right Financial Strategy Advantages and Disadvantages of Dif
Analyzing Strategic Retirement Planning Everything You Need to Know About Deferred Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Pros and Cons of Fixed Annuity Vs Equity-lin
More
Latest Posts